
Managing money is not just about saving or cutting expenses, it’s about understanding how your finances work as a whole. In Malaysia, many people struggle with debt, rising living costs, and limited savings. The solution starts with mastering the 4 pillars of personal finance in Malaysia: Assets, Liabilities, Income, and Expenses.
These four pillars form the foundation of financial literacy and wealth-building. Once you understand them, you can make better money decisions and achieve long-term financial security.
1. Assets – Building Wealth in Malaysia
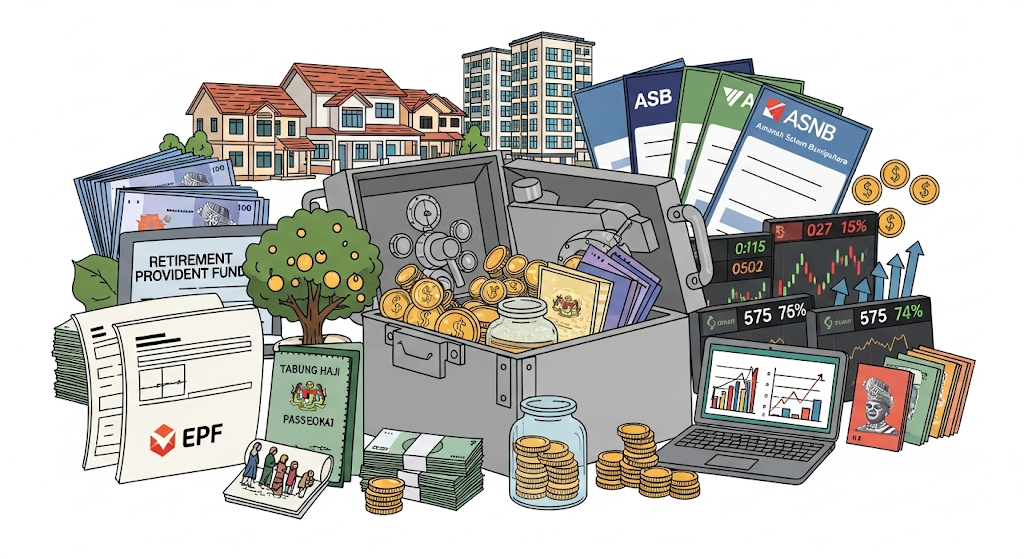

Assets are anything you own that adds value to your life or generates money for you. In personal finance, assets are the foundation of wealth creation.
Examples of assets in Malaysia include:
- EPF (KWSP) savings – your retirement fund.
- ASB / ASNB investments – steady returns for Bumiputera investors.
- Tabung Haji savings – a safe savings option for Muslims.
- Properties – houses, land, or shop lots that generate rental income.
- Stocks & Unit Trusts – investment products with long-term growth.
✅ Extra tips: Always aim to build productive assets that generate income, instead of non-productive ones like cars (which depreciate in value).
2. Liabilities – Managing Debt Wisely
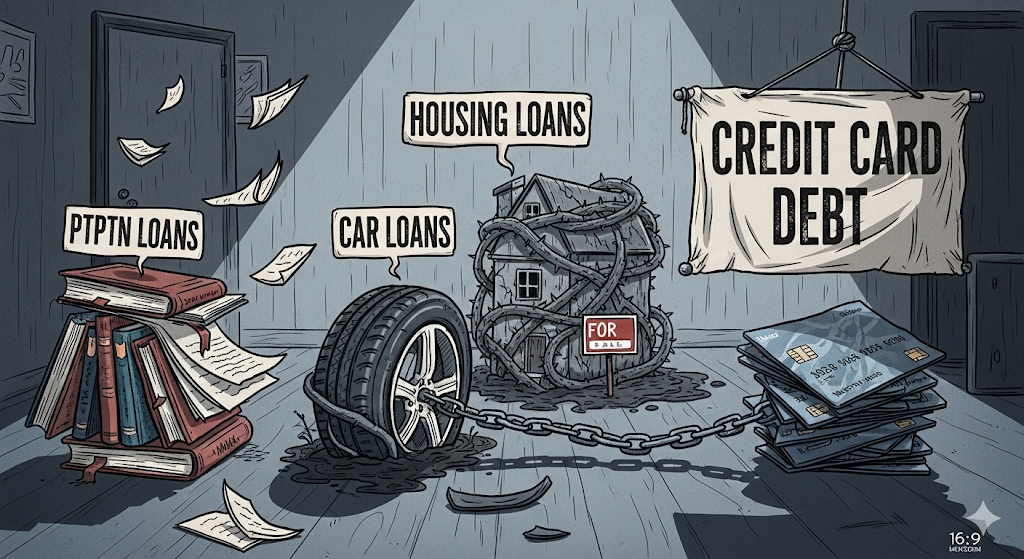
Liabilities are what you owe, your debts and financial obligations. Understanding your liabilities is critical in personal finance because too much debt weakens your financial health.
Common liabilities in Malaysia:
- PTPTN loans – common for fresh graduates.
- Car loans – necessary for most Malaysians but a depreciating liability.
- Housing loans (mortgages) – considered a “good liability” if the property appreciates.
- Credit card debt & personal financing – high-interest liabilities that drain wealth.
💡 Tip for Malaysians: Pay off high-interest debt like credit cards first. Use liabilities strategically, such as a housing loan, which can be an asset in the long run.
3. Income – The Foundation of Financial Growth
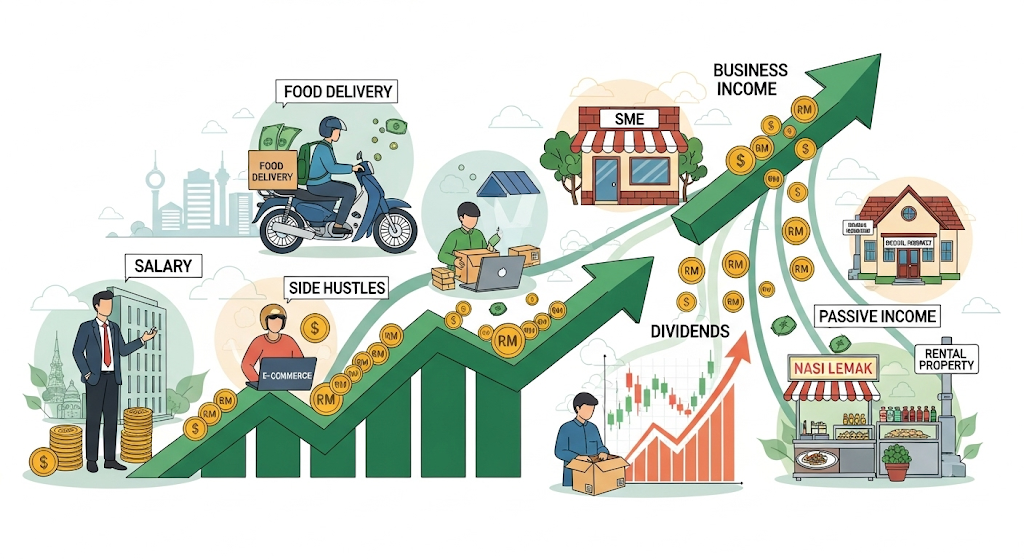
Income is the money you earn that fuels your financial journey. Without income, you can’t save, invest, or pay off liabilities.
Sources of income in Malaysia include:
- Salary & allowances – the most common for employees.
- Side hustles – freelancing, food delivery, e-commerce.
- Business income – running SMEs, food stalls, or digital businesses.
- Passive income – dividends, royalties, and rental property.
💡 Tip: Malaysians should explore multiple income streams. Relying on one salary is risky, so diversify with side hustles or investments.
4. Expenses – Controlling Your Spending
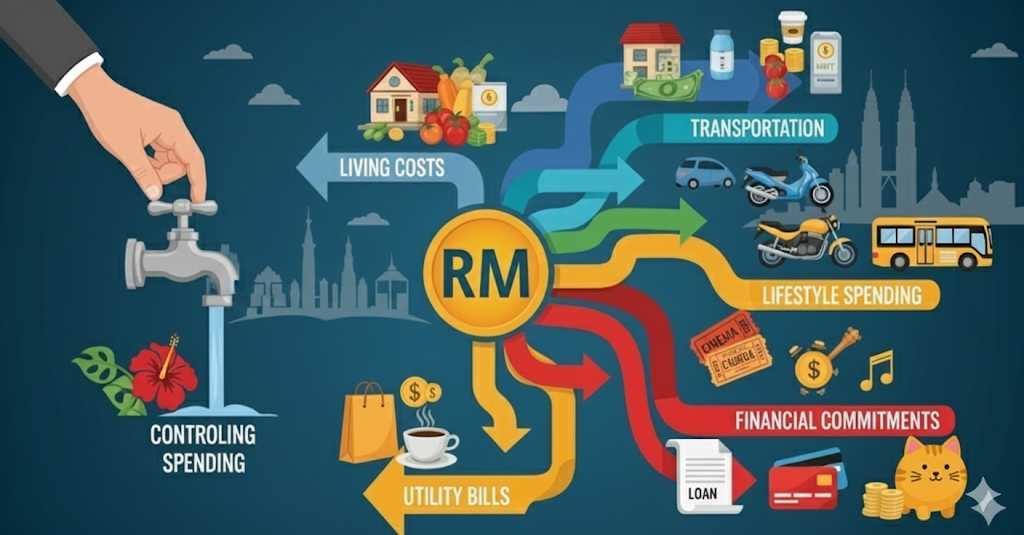
Expenses are the money that flows out of your pocket. While some are unavoidable, uncontrolled expenses prevent you from building wealth.
Typical expenses in Malaysia:
- Living costs: Rent, food, groceries, utilities.
- Transportation: Petrol, tolls, Grab, car maintenance.
- Lifestyle spending: Shopping, entertainment, dining out.
- Commitments: Insurance, children’s education, family support.
💡 Tip: Track your expenses using mobile apps like MAE by Maybank or Spendee. Apply the 50/30/20 budgeting rule:
- 20% for savings & investments
- 50% for needs
- 30% for wants
Why the 4 Pillars of Personal Finance Matter in Malaysia

When you understand Assets, Liabilities, Income, and Expenses, you gain control over your financial life. These pillars show you:
- How much wealth you are building.
- Whether you are taking on too much debt.
- If your income is enough to cover your lifestyle.
- Where your money is going every month.
This knowledge empowers Malaysians to reduce financial stress, avoid unnecessary debt, and create a sustainable path to financial freedom.
Conclusion
The 4 pillars of personal finance in Malaysia (Assets, Liabilities, Income, and Expenses) are the foundation of financial success. By increasing assets, reducing liabilities, growing income, and controlling expenses, you can achieve financial stability and long-term wealth.
